Introduction
The Yale course in the coursera.
The astonishing hypothesis:
You, your joys and your sorrows, your memories and your ambitions, your sense of personal identity and free will, are in fact no more than the behavior of a vast assembly of nerve cells and their associated molecules.
Mind = Brain -> Materialism
Descartes(1596 - 1650) proposed Dualism:
I think, therefore, I am.
Though, the radical bodily changes personal identity. See Phineas Gage.
Neurons
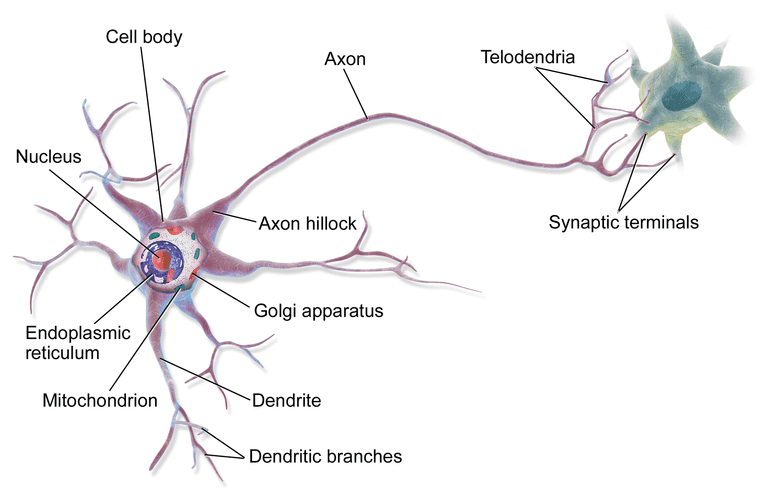
The neurons use binary, the continuality comes from the number or frequency of firing.
Parts of Brain
Subcortical structures: medulla, cerebellum, hypothalamus.
Psychology only focus on Cerebral Cortex:
- Apraxia: problem of doing actions.
- Agnosia: psychic blindness.
- Aphasia: speaking issue.
- Acquired Psychopathy.
Our two brains
Visual Crossover and motor crossover.
The left brain and right brain are connected by corpus callosum.
The mind is a computer: sensory, motor ..
The consciousness, such as subjective experience, qualia.
Sigmund Freud
Unconscious Motivation and unconscious dynamics.
Psychoanalytic division of the mind:
- Id, animalistic, according to the Pleasure Principle.
- Ego, pragmatically to reconcile your desire with the society.
- Superego: internalization of society’s moral standards.
Stage of Development
- Oral Stage: birth - 1 year, related to breast feeding.
- Anal: 1 - 3 years, pot training poorly.
- Phallic: Oedipus Complex.
- Latency: 5 - puberty, sexual feelings repressed
- Genital: puberty, sexual feelings re-emerged.
Defense Mechanism
- Displacement: redirect energy to more appropriate target.
- Sublimation: displacement activities that valued are by society.
- Projection: reducing anxiety by attributing unacceptable impulses to someone else.
- Rationalization: reasoning away anxiety-producing thoughts.
- Regression: retreating to a mode of behavior of earlier stage.
- Reaction formation: replacing threating wishes with their opposites.
Scientific assessment
Falsifiability. But the core of Freuds, the unconsciousness is intact.
B.F. Skinner
Theory of behaviorism:
- Emphasis on learning
- Anti-mentalism: stimulation -> response.
- No differences across species
Habituation: A decline in the tendency to respond to familiar stimuli.
Classical conditioning: Association between one stimulus and another. Ivan Pavlov.
reinforced trials vs. unreinforced trials.
Instrumental Conditioning: shaping the approximated behaviors by rewarding.
Schedule of reinforcement:
- fixed ratio
- variable ratio: slot machine
- fixed interval
- variable interval
Scientific assessment of Skinner
Emphasis on learning: unlearned knowledge exists.Anti-Mentalist: Observables are discussed in general.No differences across species: animals are different in learning.
Chomsky says the behaviorism false or empty such as the reinforcement is too vague.